OpenAPI Schemas
Yaat can generate OpenAPI specification for API schemas.
It looks through routes and read the docstrings to generate documentation. By default, the route will be not in the generated schema, you will have to set has_schema=True to indicate the route has a schema.
Signature
OpenAPISchema(title: str, description: str = None, version: str = None)
from yaat import Yaat
from yaat.openapi import OpenAPISchema
from yaat.responses import JSONResponse
app = Yaat()
openapi = OpenAPISchema("Yaat", "API documentation", "1.0")
@app.route("/schema")
async def api(request):
return openapi.Response(request)
@app.route("/users", has_schema=True)
async def users(request):
"""
responses:
200:
description: List users.
examples:
[{"name": "Jane Doe"}]
"""
return JSONResponse(["name": "Jane Doe"])
You can access the OpenAPI schema at /schema.
openapi.Responsereturn the response inapplication/vnd.oai.openapimedia-type.
If you want in JSON, useopenapi.JSONResponseinstead.
If you want to get the schema data, you can call .get_schema(routes)
router = request.app.router
schema = openapi.get_schema(router.routes)
assert schema == {
"openapi": "3.0.0",
"info": {
"title": "Yaat",
"description": "API documentation",
"version": "1.0"
},
"paths": {
"/users": {
"get": {
"responses": {
"200": {"description": "List users."}
},
"examples": [{"name": "Jane Doe"}]
},
},
},
}
Swagger UI
Yaat also has a handler to get Swagger UI.
Signature
get_swagger_ui(
*,
openapi_url: str,
title: str,
swagger_favicon_url: str = DEFAULT_FAVICON_URL,
)
from yaat import Yaat
from yaat.responses import TextResponse
from yaat.openapi import OpenAPISchema, get_swagger_ui
app = Yaat()
openapi = OpenAPISchema("Yaat", "API documentation", "1.0")
@app.route("/openapi")
async def api(request):
return openapi.Response(request)
@app.route("/swagger")
async def index(request):
return get_swagger_ui(openapi_url="/openapi", title="Yaat")
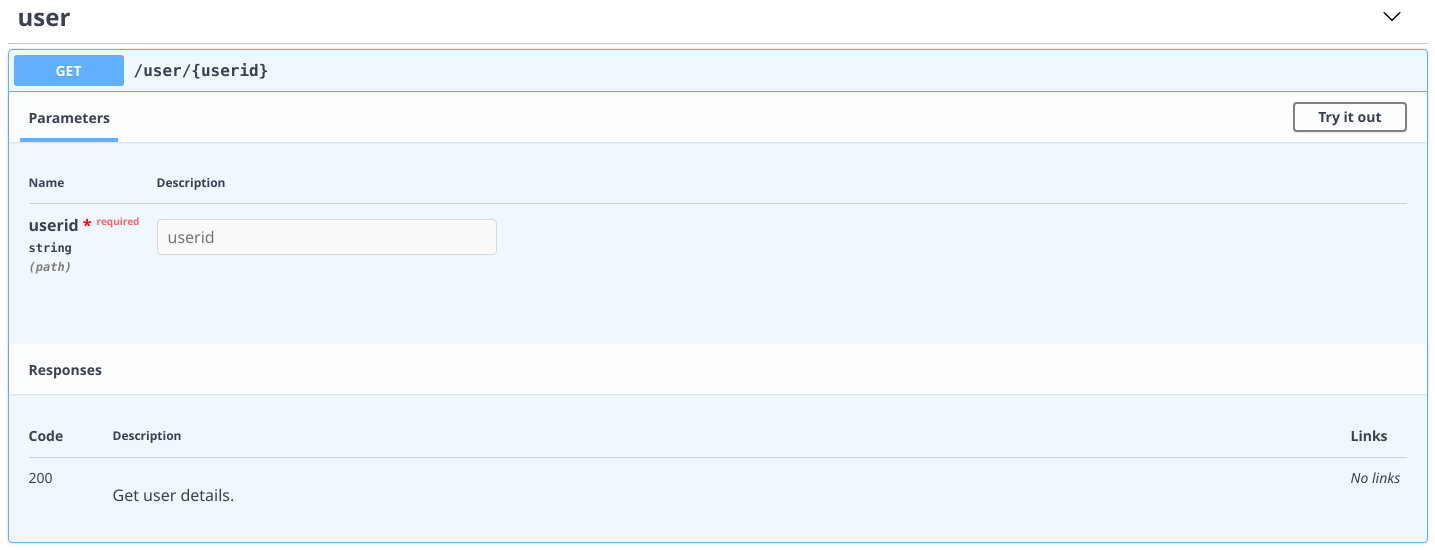
@app.route("/user/{userid}", has_schema=True)
async def get_user(request, userid: str):
"""
responses:
200:
description: Get user details.
"""
return TextResponse(f"This is {userid}.")
You can access the OpenAPI schema at /swagger.
-
If you do not specify path parameters, Yaat will look at the handler's parameters and add the specification automatically. However, you can also override that by specifying inside docstrings.
-
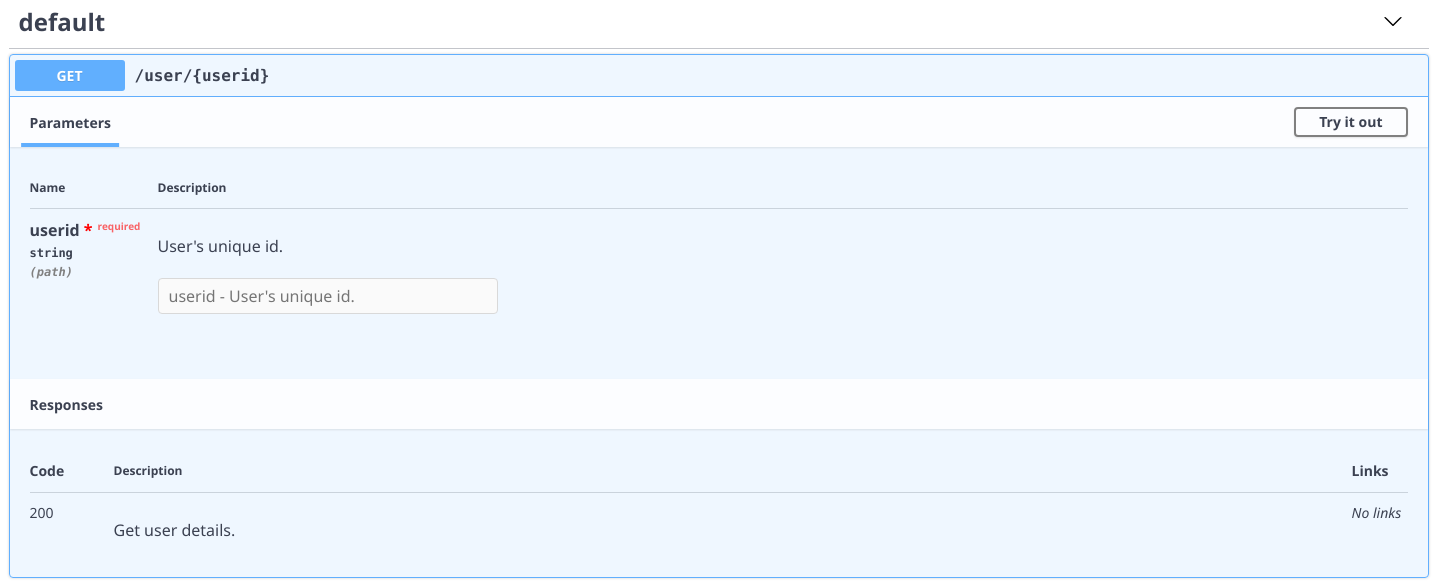
If you also want to specify the description for the path parameter, you can write it inside the docstring.
@app.route("/user/{userid}", has_schema=True)
async def get_user(request, userid: str):
"""
parameters:
- name: userid
description: User's unique id.
responses:
200:
description: Get user details.
"""
return TextResponse(f"This is {userid}.")
-
If you do not put the default value for the parameter, it will be
requiredin documentation. -
For the value type, it determines by Python's type hinting.
int- will be integer.float- will be number.bool- will be boolean.str- will be string.
Also if the type is not from the above, it will be
string.
Tags
You can add tags to your routes. They will be added to the OpenAPI schema and routes with the same tag will be grouped in Swagger UI.
tags- a list of strings, commonly just one string inside.
@app.route("/user/{userid}", has_schema=True, tags=["user"])
async def get_user(request, userid: str):
"""
responses:
200:
description: Get user details.
"""
return TextResponse(f"This is {userid}.")